ExaWizards Launches their “exaBase Vision Simulator”, A Service for Improved Performance of Image Recognition AI Models.
RIKEN to Use the Alpha Version in its Guardian Robot Project
ExaWizards Inc., a company that develops AI-enabled services to solve social issues (Headquarters:Minato-ku, Tokyo; Representative Director & President: Ko Ishiyama; hereafter, “ExaWizards”) announces alpha launch of the “exaBase Vision Simulator,” a synthetic image generation service that helps to significantly reduce the cost of image data collection for AI model development with improved precision.
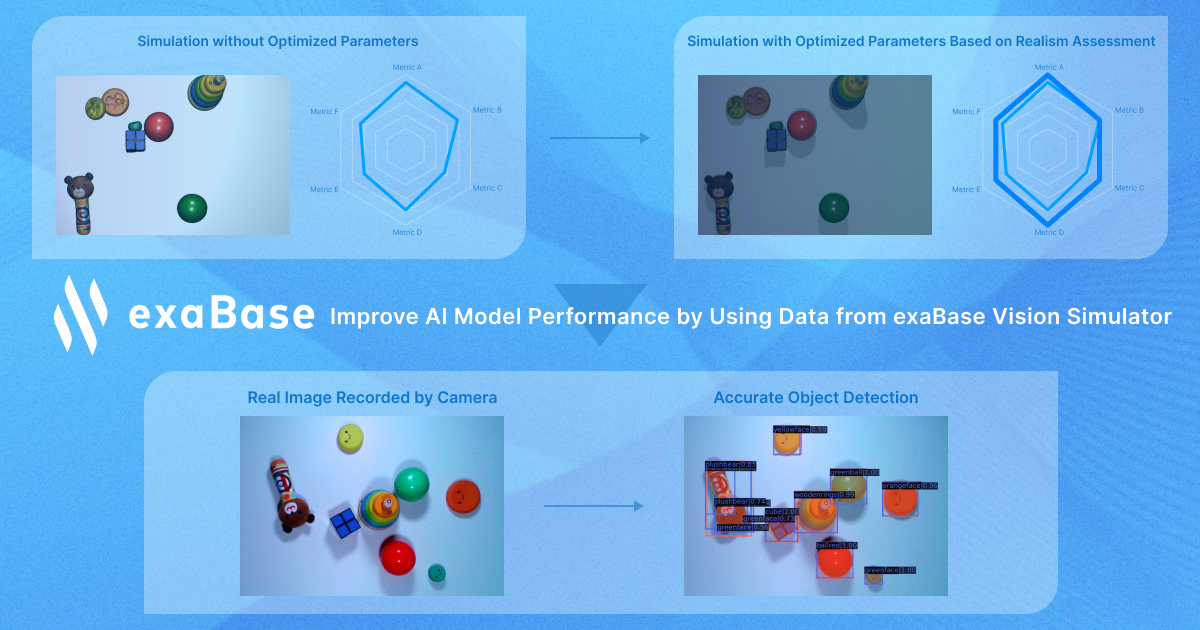 ☑︎Improve the Realism of the Synthetic Images Generated by Simulators
☑︎Improve the Realism of the Synthetic Images Generated by Simulators
AI model training requires large amounts of data. In many cases, real data collection cost is prohibitively high and additionally increases the duration of AI development project. Therefore, researchers and engineers have attempted to automatically generate synthetic data using simulation technologies for many years. However, many of these synthetic image attempts lacked realism, resulting in poor performance of the AI models developed.
The “exaBase Vision Simulator” by ExaWizards can significantly reduce data collection cost for image recognition AI models and, hence, the development. With it, data collection can be completed in mere days, whereas real image-based data collection may take several weeks to finish. This is expected to significantly improve the productivity of AI model development teams.
From 3D mesh data, the “exaBase Vision Simulator” generates a huge volume of synthetic image data with annotation necessary for image recognition AI models. Also, it can evaluate the realism of the generated images using ExaWizard’s realism assessment framework. By adjusting rendering parameters based on this framework, the “exaBase Vision Simulator” can quantitatively evaluate and decide how to generate realistic synthetic images (Patent No. 7058434). This way, users can generate synthetic images with higher realism and quickly develop accurate recognition AI models.
☑︎Achieve Up To 3.6 Points Higher Precision in Comparison with Models Trained with Conventional Synthetic Images
It was verified that object detection AI models developed using the “exaBase Vision Simulator” can achieve up to 3.6 points higher precision*1 in comparison with those trained with conventional synthetic images using our environment. Also, we are investigating various post-processing algorithms based on the framework to further improve the realism of generated synthetic images and the performance of resulting AI models.
The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (RIKEN) has decided to use the alpha version of the “exaBase Vision Simulator” in its Guardian Robot Project, and to test it in an object recognition algorithm on the camera attached to “Butsukusa-kun,” a prototype robot in the project*2.
[Use Cases]
The “exaBase Vision Simulator” can be used not only for the automation of robotic tasks that involve image recognition such as robotic piece picking or packaging, but also in a wide range of fields including autonomous agricultural vehicles, autonomous cars, AI cameras, visual inspections, and R&D activities within companies and universities. As described below, this new service can give a solution to problems that are currently difficult to solve through the deployment of AI models.
1. When you use image recognition AI models, it takes significant labor-hours to collect data that matches a specific scene, which hinders the smooth deployment of AI models. In such cases, the “exaBase Vision Simulator” enables the creation of datasets for a particular scene in a short time.
2. When you use public data or other real data for AI model training, the license terms may prohibit commercial use or the data may include personal identifiable information(PII), which requires strict control. In such cases, the “exaBase Vision Simulator” enables the creation of datasets for commercial use or data excluding PII.
3. When you develop an AI model for a visual inspection, you may find it difficult to make the model accurate enough since the volume of available data with anomalies is too small. In such cases, the “exaBase Vision Simulator” enables the creation of data with a sufficient occurrence of anomalies to improve the performance of the AI model.
Our engineers Arturo Ceron-Lopez, Rahul Ranjan and Nishanth Koganti described some of the key technologies in their paper “Realism Assessment for Synthetic Images in Robot Vision through Performance Characterization.” The paper has been accepted for publication in “IROS 2022,”*3 a prestigious international conference in robotics, and will be presented at Kyoto International Conference Center in October 2022.
*1: Evaluated using “mAP (mean average precision)”, an index commonly used for the object detection.
*2: Guardian Robot Project conducted by RIKEN promotes R&D for the social implementation of next-generation robots (“brain x AI”) that synergistically incorporate the strengths of psychology, brain science, cognitive science and AI research toward a future society where humans, AI and robots can flexibly coexist. Conventional robots have mostly performed only limited tasks based on detailed instructions from humans. However, this project aims to develop a robot that can autonomously recognize its environment and the state of the person it is supposed to support and provide assistance unobtrusively without compromising the autonomy of the person, with appropriate interaction.
URL for reference: https://grp.riken.jp/
*3: “IROS” IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems
*exaBase is a registered trademark of ExaWizards.
[ExaWizards Corporate Profile]
Company name: ExaWizards Inc.
Location: 21F, Shiodome Sumitomo Bldg., 1-9-2, Higashi Shimbashi, Minato-ku, Tokyo
Founded in: February 2016
Representative: Ko Ishiyama, Representative Director & President
Description of business: Industrial innovation and resolution of social issues through development of AI-enabled services
Corporate site: https://exawizards.com/